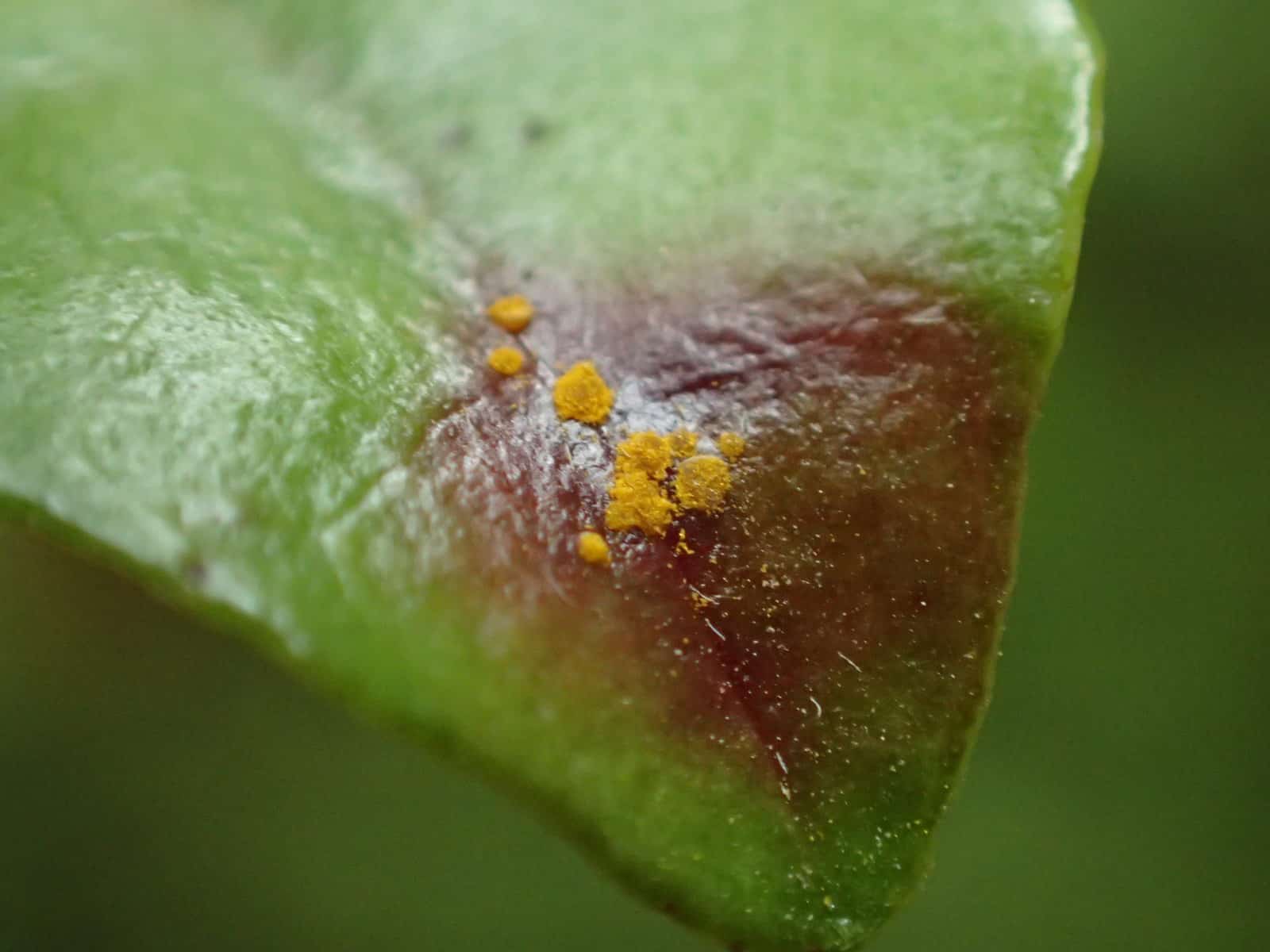
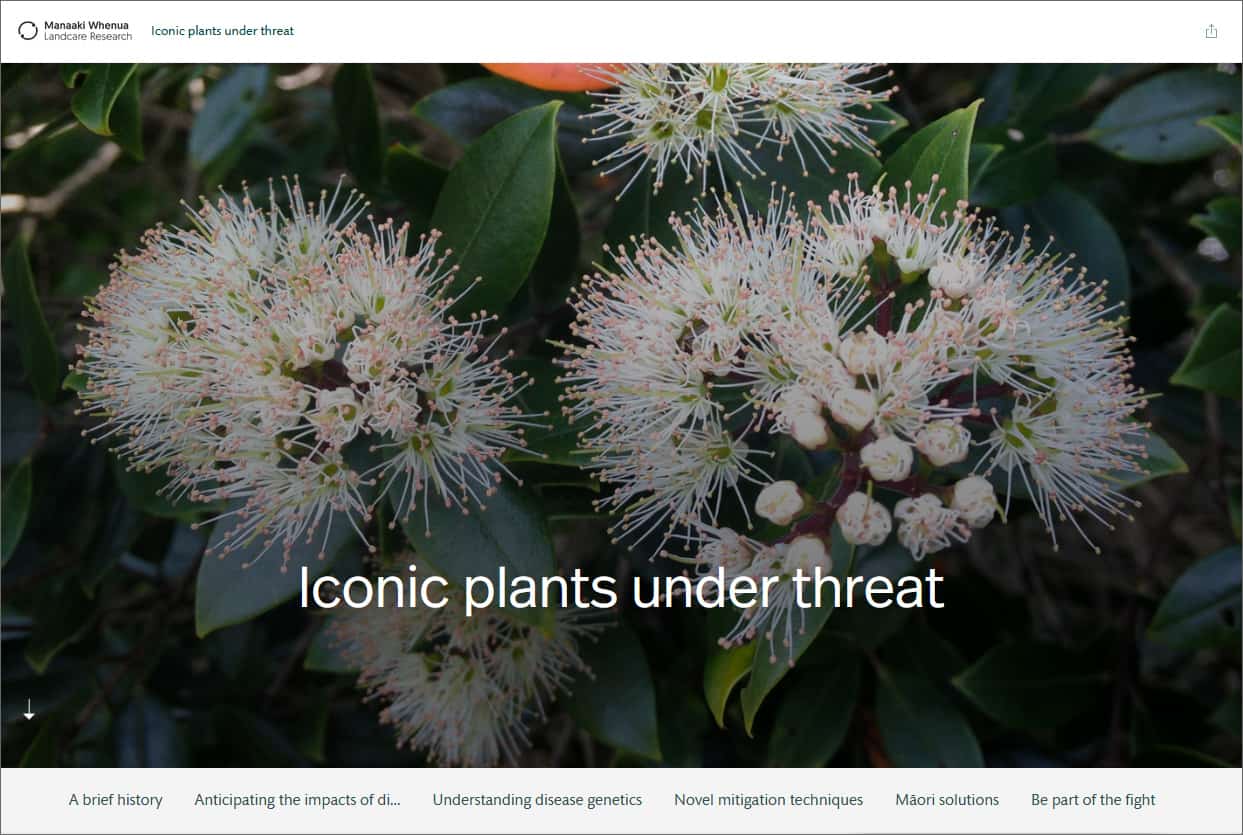
Austropuccinia psidii, causing myrtle rust, has a gigabase-sized genome shaped by transposable elements
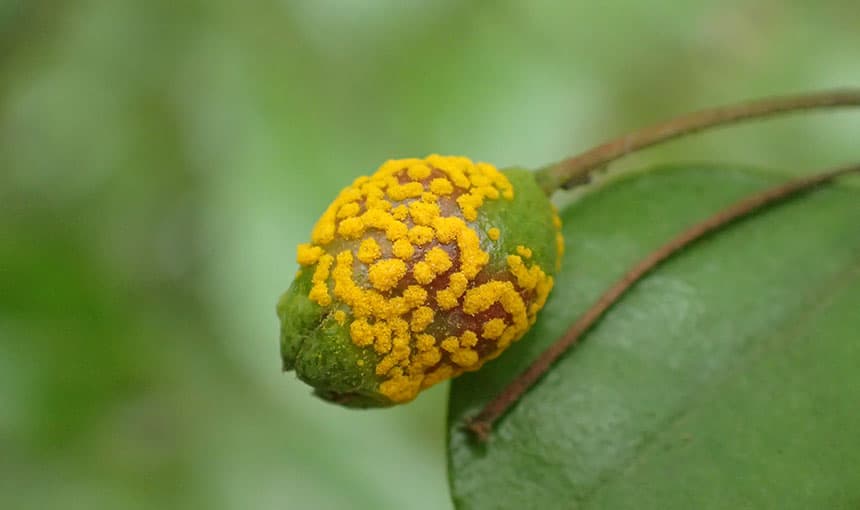
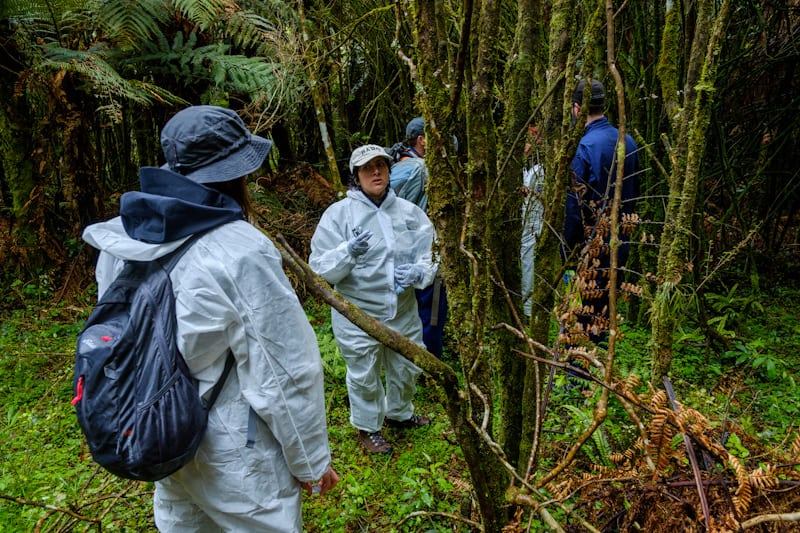
Austropuccinia psidii has a broad host range with more than 480 myrtaceous species. Since first detected in Australia in 2010, the pathogen has caused the near…